Preventive health screenings play a critical role in detecting diseases early, often before symptoms appear. Many serious conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer, are easier to treat when caught early.
While recommended screenings may vary by age, sex, family history, and lifestyle, some tests are important at every stage of life. Staying up to date with preventive screenings can help you protect your long-term health and reduce the risk of complications.
Below are 15 essential preventive health screenings you shouldn’t skip, regardless of age.
1. Blood Pressure Screening
High blood pressure (hypertension) often has no symptoms but significantly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Regular blood pressure checks help identify elevated readings early so lifestyle changes or treatment can begin before serious damage occurs.
How often: At least once every 1–2 years, or more often if readings are elevated.

2. Cholesterol Screening
High cholesterol contributes to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
A simple blood test measures total cholesterol, LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, HDL (“good”) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
How often: Every 4–6 years for healthy adults; more frequently if you have risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease.

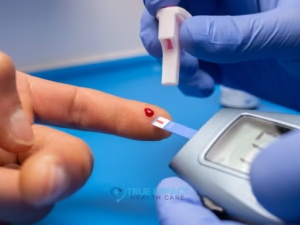
3. Blood Glucose (Diabetes) Screening
Screening for diabetes or prediabetes helps identify abnormal blood sugar levels early.
Early detection allows for lifestyle changes that may prevent or delay the development of type 2 diabetes and its complications.
How often: Every 3 years starting in adulthood, or earlier if you are overweight or have risk factors.
4. Body Mass Index (BMI) and Waist Circumference
BMI and waist measurements help assess body fat and risk for conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
While BMI is not a perfect measure, it provides useful insight when combined with other health indicators.
How often: At routine medical visits.

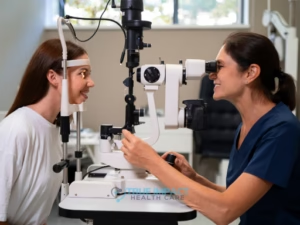
5. Vision Screening
Eye exams can detect vision problems as well as early signs of conditions such as glaucoma, cataracts, and diabetic eye disease.
Good vision is essential for daily functioning and safety at all ages.
How often: Every 1–2 years, depending on age and eye health.
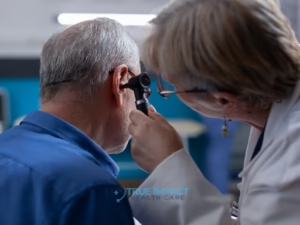
6. Hearing Screening
Hearing loss can develop gradually and may go unnoticed for years.
Early detection helps prevent communication difficulties, social isolation, and cognitive decline, particularly in older adults.
How often: Periodically throughout adulthood, especially if you notice changes in hearing.
7. Dental Exams and Oral Cancer Screening
Regular dental visits help prevent cavities, gum disease, and tooth loss. Dentists also screen for oral cancers during routine exams.
Oral health is closely linked to overall health, including heart health.
How often: Every 6–12 months.

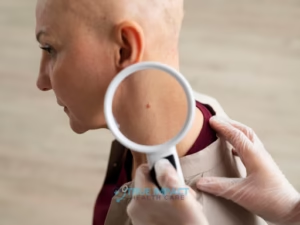
8. Skin Cancer Screening
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers, but it is highly treatable when detected early.
Self-exams and professional skin checks can help identify suspicious moles or changes.
How often: Monthly self-exams; professional exams as recommended, especially if you have risk factors.
9. Cervical Cancer Screening (Pap Test / HPV Test)
Cervical cancer screening detects abnormal cell changes before cancer develops.
HPV testing can identify high-risk strains associated with cervical cancer.
How often: As recommended by a healthcare provider, depending on age and test type.
10. Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer screening helps detect cancer early, when treatment is most effective.
Screening recommendations may vary based on age, family history, and personal risk.
How often: As advised by a healthcare provider.

11. Colorectal Cancer Screening
Colorectal cancer often develops without symptoms in early stages.
Screening tests can detect precancerous polyps or early cancers, significantly reducing mortality.
How often: Beginning in adulthood and continuing at regular intervals, depending on test type and risk factors.

12. Bone Density Screening
Bone density tests assess bone strength and help identify osteoporosis, a condition that increases fracture risk.
Early detection allows for interventions that strengthen bones and prevent fractures.
How often: As recommended, particularly for older adults or those with risk factors.
13. Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) Screening
Many STIs have no symptoms but can cause long-term health complications if left untreated.
Screening supports early treatment and helps prevent transmission.
How often: Based on sexual activity, risk factors, and healthcare guidance.

14. Mental Health Screening
Mental health is a key component of overall well-being.
Screenings for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions can help identify concerns early and connect individuals with appropriate support.
How often: During routine healthcare visits or whenever symptoms arise.

15. Immunization Review
Vaccinations are a cornerstone of preventive care at every age.
Regular immunization reviews ensure protection against preventable diseases, including influenza, tetanus, and other infections.
How often: At routine healthcare visits.

Why Preventive Screenings Matter
Preventive screenings:
-
Detect diseases early
-
Reduce healthcare costs over time
-
Improve quality of life
-
Support longer, healthier lives
Skipping screenings may allow silent conditions to progress unnoticed, increasing the risk of complications.
How to Stay on Track With Preventive Care
-
Schedule annual checkups
-
Keep a personal health record
-
Discuss family medical history with your provider
-
Ask which screenings are right for you
-
Follow up on abnormal results promptly
Final Thoughts
Preventive health screenings are one of the most effective ways to protect your health at any age. Staying proactive allows you to catch potential problems early, make informed decisions, and take control of your long-term well-being.
Always consult a healthcare provider to determine which screenings are most appropriate based on your individual health needs.










One Response